This example shows how to build the required data files and then extract the daily rainfall at two sites. Here, one of the sites is at a rainfall gauge and the results are compared against observations.
Make netCDF file
The first step is to create the netCDF files. Here only one netCDF file is created and only for precipitation data (as defined by the following URLS for the source data being set to NA: urlTmin, urlTmax, urlVprp, urlSolarrad) and only between the dates updateTo and updateTo. If the latter two dates were not input then data would be downloaded from 1/1/1900 to yesterday.
The netCDF file contains grids of daily rainfall for all of Australia and is used below to extract data at points of interest. Often users run makeNetCDF_file once to build netCDF data files that contain all variables over the entire record length (which requires ~5GB disk storage) and then use the netCDFs grids for multiple projects, rather than re-building the netCDF for each project. Also, if makeNetCDF_file is run with the the netCDF file names pointing to existing files and updateFrom=NA then the netCDF files will be updated to yesterday.
To start to create the grids, the file name for the netCDF grids need to be defined. Here we’ll just use temporary files. You should change this to a non-temporary file name and folder.
# Set names for netCDF files (in the system temp. directory).
ncdfFilename = tempfile(fileext='.nc')
fnames = makeNetCDF_file(ncdfFilename = ncdfFilename,
updateFrom=as.Date("2010-08-01","%Y-%m-%d"),
updateTo=as.Date("2010-10-01","%Y-%m-%d"),
urlTmin=NA, urlTmax=NA, urlVprp=NA, urlSolarrad=NA)
#> Starting to build both netCDF files.
#> ... Testing downloading of AWAP precip. grid
#> ... Getting grid gemoetry from file.
#> ... Deleting /home/runner/work/AWAPer/AWAPer/vignettes/precip.20000101.grid.gz
#> ... Building AWAP netcdf file.
#> NetCDF data will be updated from 2010-08-01 to 2010-10-01
#> ... Downloading non-solar data and importing to netcdf file:
#> Warning in makeNetCDF_file(ncdfFilename = ncdfFilename, updateFrom =
#> as.Date("2010-08-01", : Note, the solar radiation data netCDF file will not be
#> built or updated.
#> Data construction FINISHED.
#> Total run time (DD:HH:MM:SS): 00:00:00:45Set the points for data extraction
Set coordinates to the location of one groundwater bore and one rainfall gauge and then convert the points to a spatial object and set projection to GDA94.
coordinates.data = data.frame( ID =c('Bore-10084446','Rain-63005'),
Longitude = c(153.551875, 149.5559),
Latitude = c(-28.517974,-33.4289))
sp::coordinates(coordinates.data) <- ~Longitude + Latitude
sp::proj4string(coordinates.data) = '+proj=longlat +ellps=GRS80 +no_defs'Extract daily precipitation data
Extract the daily precipitation at the two locations. The data is extracted from the netCDF file ncdfFilename and between the dates extractFrom and extractTo.
The other AWAPer variables are not extracted because getTmin, getTmax, getVprp, getSolarrad and getET are set to F. Note the netCDF file ncdfFilename must be in the working directory or the full file path must be given.
climateData.data = extractCatchmentData(ncdfFilename=ncdfFilename,
extractFrom=as.Date("2010-08-01","%Y-%m-%d"),
extractTo=as.Date("2010-10-01","%Y-%m-%d"),
locations=coordinates.data,
getTmin=F, getTmax=F, getVprp=F, getSolarrad=F, getET=F)
#> Extraction data summary:
#> NetCDF non-solar radiation climate data exists from 2010-08-01 to 2010-10-01
#> Data will be extracted from 2010-08-01 to 2010-10-01 at 2 locations
#> Starting data extraction:
#> ... Building catchment weights
#> ... Starting to extract data across all locations:
#> ... Calculating area weighted daily data.
#> Data extraction FINISHED.
#> Total run time (DD:HH:MM:SS): 00:00:00:05Plot the daily precipitation at each site
Plot time series of the etracted daily precipitation.
for (i in 1:nrow(coordinates.data)){
filt = climateData.data$CatchmentID.ID == coordinates.data$ID[i]
data2plot = climateData.data$precip_mm[filt]
dates = ISOdate(climateData.data$year[filt],climateData.data$month[filt],climateData.data$day[filt])
if (i==1){
plot(dates, data2plot, main='Extracted precip.', ylab='Precip [mm/d]', xlab='Date [day/month]', type='l',lty = i+1, cex=0.2)
} else {
lines(dates, data2plot, lty = i+1)
}
}
legend('topright',legend=c('Bore-10084446','Rain-63005'),lty=2:3)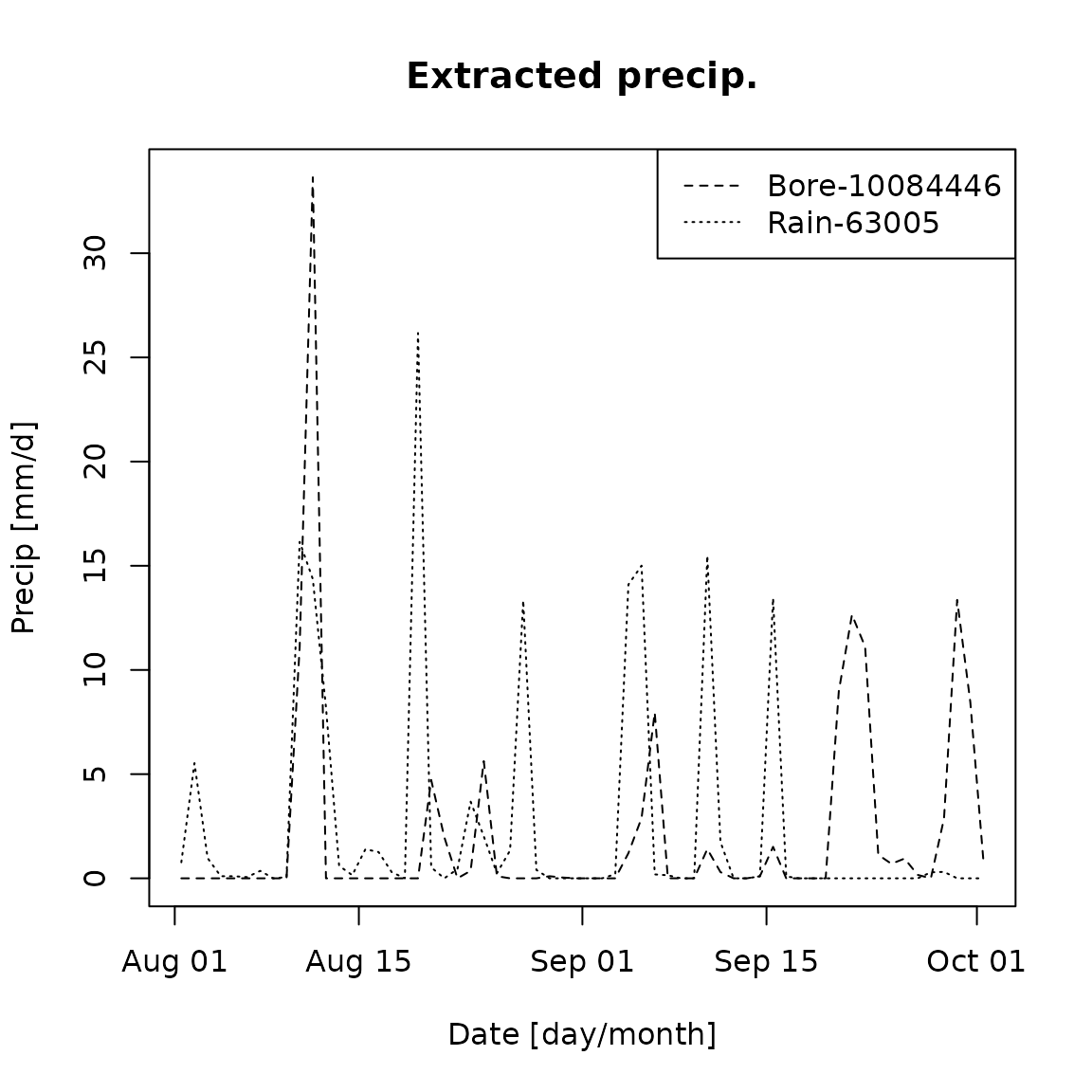
Check AWAPer data against precipitation gauge date
Use the following observed precipitation (from gauge_63005) to check the AWAPer data.
First let’s hard-code in and sourced from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology.
obsPrecip <- data.frame(
year= c(2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010,
2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010,
2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010),
month = c(8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9,
9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 9, 10),
day = c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 1),
precip_mm = c(0.6, 5.2, 0.8, 0.4, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 15.8, 15.6, 7.6, 0.7, 0.4, 1.4, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 30.4, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 5.0, 2.2, 0.3, 0.8, 13.8, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 13.8, 15.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 12.4, 0.9,
0.0, 0.0, 0.1, 13.0, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.3, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0))Now let’s compare the extracted rainfall against the gauge rainfall data.
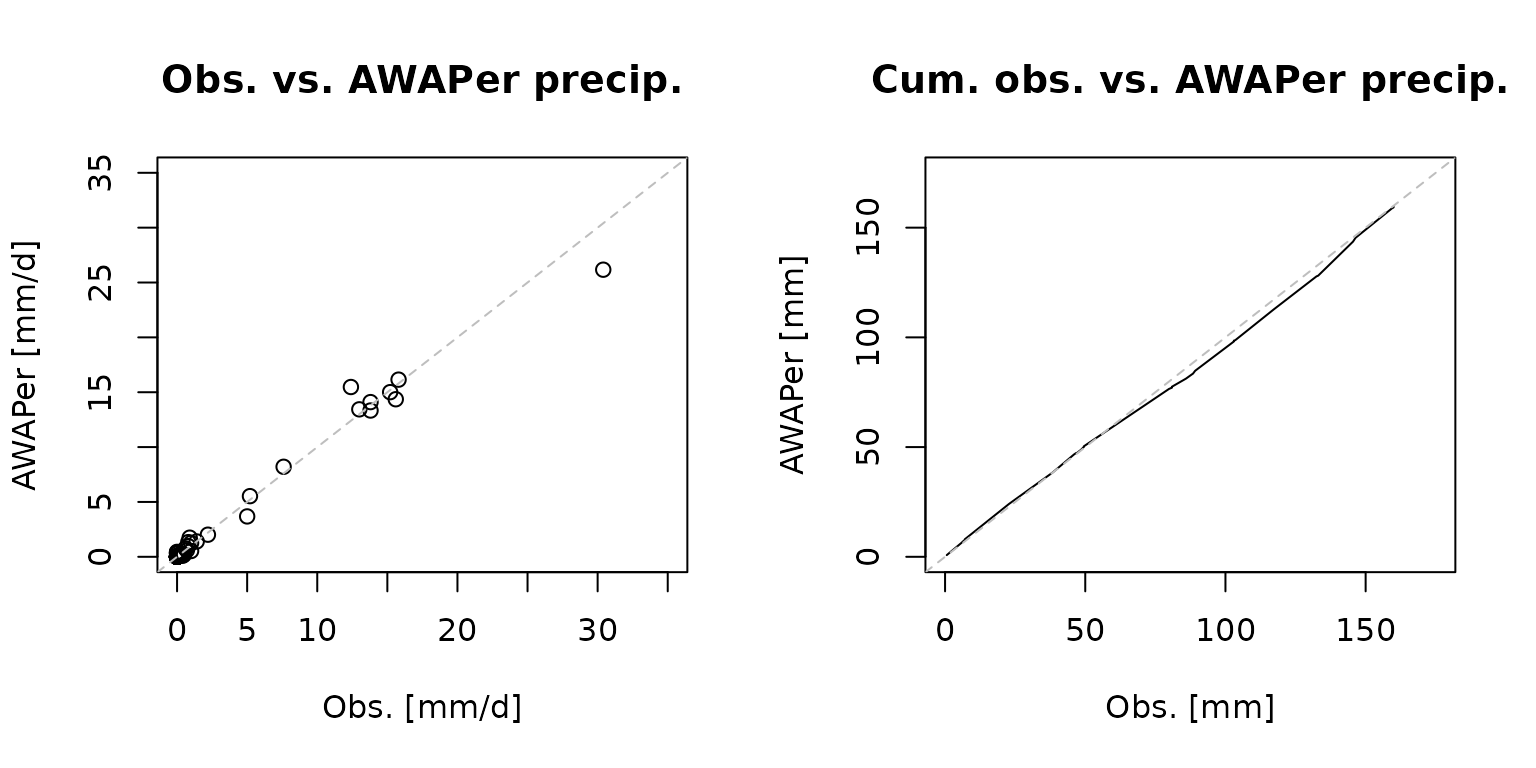
The left plot shows that the gauge and extracted data plot along the 1:1. This shows that the extracted data is unbiased. The scatter does, however, show that there is some difference in the estimates. This arises because the source grids are at a 0.05 degree resolution, or about 5 km x 5 km, and this introduces some error with the gauge is not at the centre of the grid cell and the location to be extracted is not also at the centre.
par(mfrow = c(1, 2))
filt2 = climateData.data$CatchmentID.ID=='Rain-63005'
plot(obsPrecip$precip_mm,climateData.data$precip_mm[filt2],
xlim = c(0,35),ylim = c(0,35),
main='Obs. vs. AWAPer precip.',
xlab='Obs. [mm/d]', ylab='AWAPer [mm/d]', cex=1)
abline(0,1, col='grey', lty=2)
plot(cumsum(obsPrecip$precip_mm),cumsum(climateData.data$precip_mm[filt2]),
xlim = c(0,175),ylim = c(0,175),
main='Cum. obs. vs. AWAPer precip.',
xlab='Obs. [mm]', ylab='AWAPer [mm]', type='l', cex=1)
abline(0,1, col='grey', lty=2)